The Bunya Pine: A Strange, Impressive, and Useful Tree..
What Is a Bunya Pine?
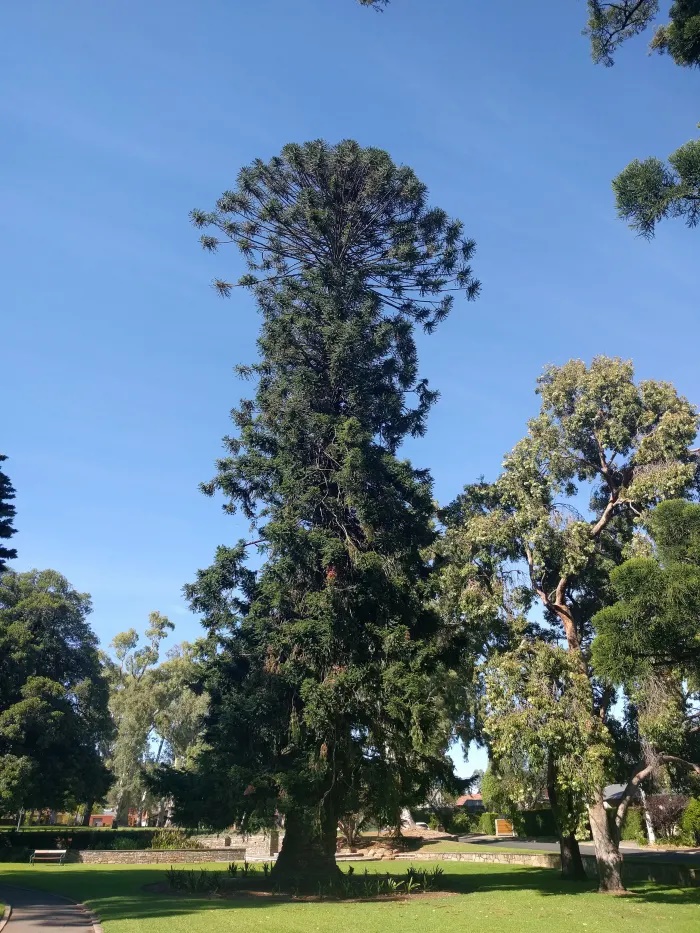
The bunya pine, or Araucaria bidwillii, is famous for its huge cones and its delicious seeds. It's a relative of the monkey puzzle tree, another curious plant. Like its relative, the bunya pine is an evergreen conifer that has an unusual branching pattern, strange leaves, and edible seeds inside a large cone. Even the smaller female cones are the size of a bowling ball. Some can be as large as a person's head. It's often dangerous to be under a tree when it's dropping its cones.
The bunya pine tree is native to Queensland in northeastern Australia and belongs to the family Araucariaceae. The family was widespread in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Its members existed in both the northern and southern hemisphere and coexisted with dinosaurs. Today the family is restricted to the southern hemisphere, except for cultivated specimens, but its members still have unique features that are sometimes described as "reptilian".
Based on its common name, we might assume that the bunya pine is a type of pine tree. This isn't the case, however. The bunya pine belongs to the family Araucariaceae. Pine trees belong to the family Pinaceae. Both families belong to the order Pinales, so they are distant relatives.Unusual Trunk and Branches
A bunya pine tree may reach a height of 45 meters (about 148 feet), a diameter of 1.5 meters (around 4 feet), and a spread of 15 meters (49 feet). Further examinations of the trees may lead to changes in these numbers. The fully-grown tree is certainly large, however.
The thick and sturdy trunk is very straight and is brown to black in color. It has a horizontally furrowed bark. In older trees, the furrows may be deep. The trunk is often said to resemble the leg of an elephant or a dinosaur in appearance.
The branches of a bunya pine have a strange appearance. They are arranged around the trunk in whorls. They are bare except for a dense tuft of small secondary branches at their tips, which bear spiky leaves.
The immature tree is shaped like a pyramid. As it matures, it loses some of its lower branches and develops a dome-shaped crown at the upper part of the trunk. After the lower branches drop, shorter whorls of branches often develop from dormant buds below the domed crown. This sometimes gives the tree a two-tiered appearance.