A Night Rainbow Lit By the Moon?
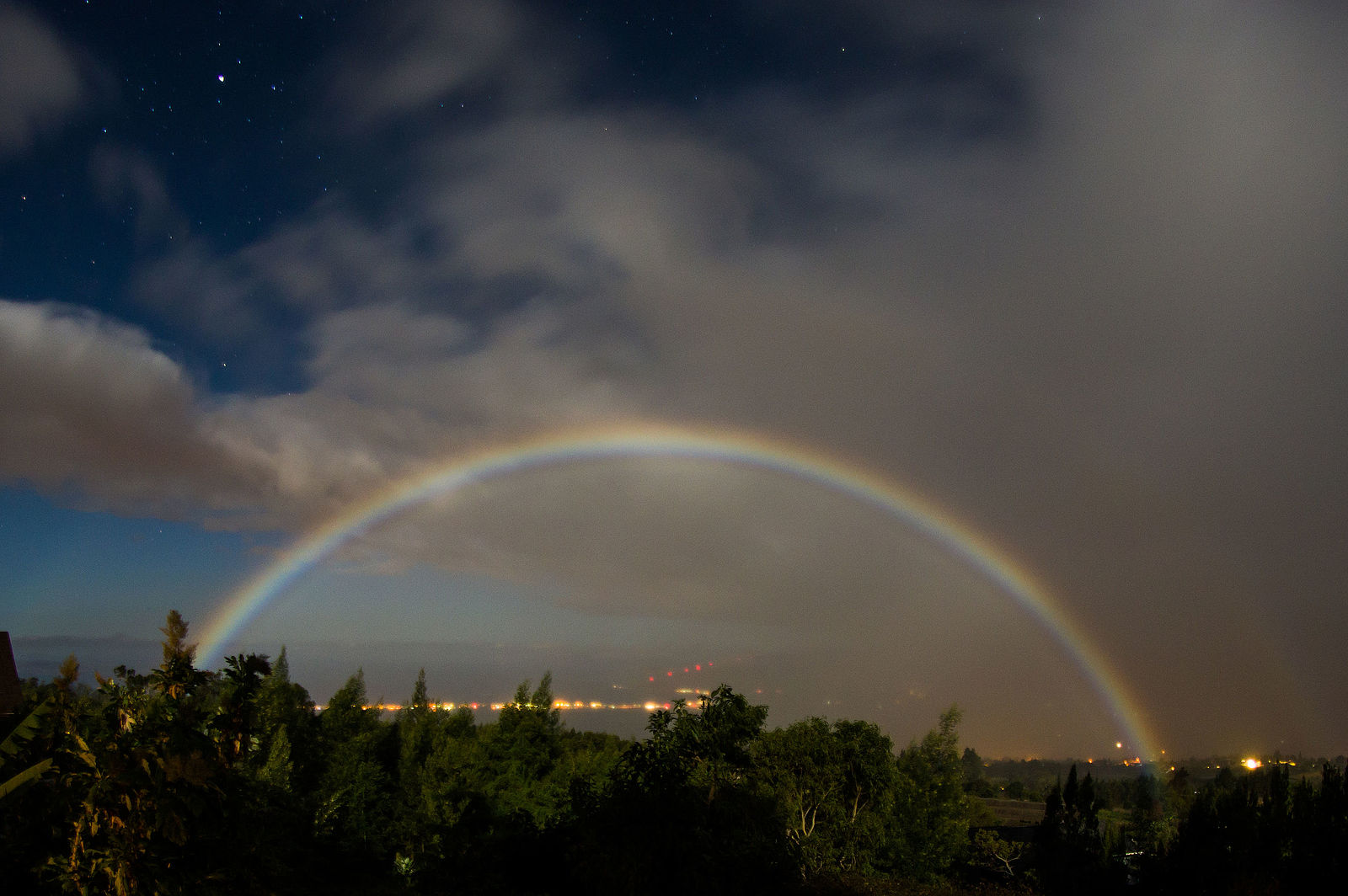
Lunar rainbow over Kihei, Maui, Hawaii, US. Image credit: Arne-kaiser
Moonbows are best viewed at and around full moon, when the Moon is at or nearest to its brightest phase and is not obscured by clouds. For moonbows to to appear, the Moon must be low in the sky (at an elevation of less than 42 degrees, preferably lower) and the night sky must be very dark. But since the sky is not completely dark on a rising/setting full moon, moonbows can only be observed two to three hours before sunrise, or two to three hours after sunset. And, of course, there must be water droplets (e.g. from rain or spray) in the sky, opposite the Moon.
This set of requirements makes moonbows much rarer than solar rainbows – they actually occur less than 10 percent as often as normal rainbows. Sometimes moonbows can also be observed during full moonrise during the winter months, when the sky is darker and rain falls at extreme latitudes. The definition of the colors is subject to the size of moisture drops present in the air: the smaller they are the less vivid the colors will be.
Moonbows are best viewed at and around full moon, when the Moon is at or nearest to its brightest phase and is not obscured by clouds. For moonbows to to appear, the Moon must be low in the sky (at an elevation of less than 42 degrees, preferably lower) and the night sky must be very dark. But since the sky is not completely dark on a rising/setting full moon, moonbows can only be observed two to three hours before sunrise, or two to three hours after sunset. And, of course, there must be water droplets (e.g. from rain or spray) in the sky, opposite the Moon.
This set of requirements makes moonbows much rarer than solar rainbows – they actually occur less than 10 percent as often as normal rainbows. Sometimes moonbows can also be observed during full moonrise during the winter months, when the sky is darker and rain falls at extreme latitudes. The definition of the colors is subject to the size of moisture drops present in the air: the smaller they are the less vivid the colors will be.
Advertisements
13 December 2023
Advertisements