Ammolite: Gemstone with Iridescent Colors!
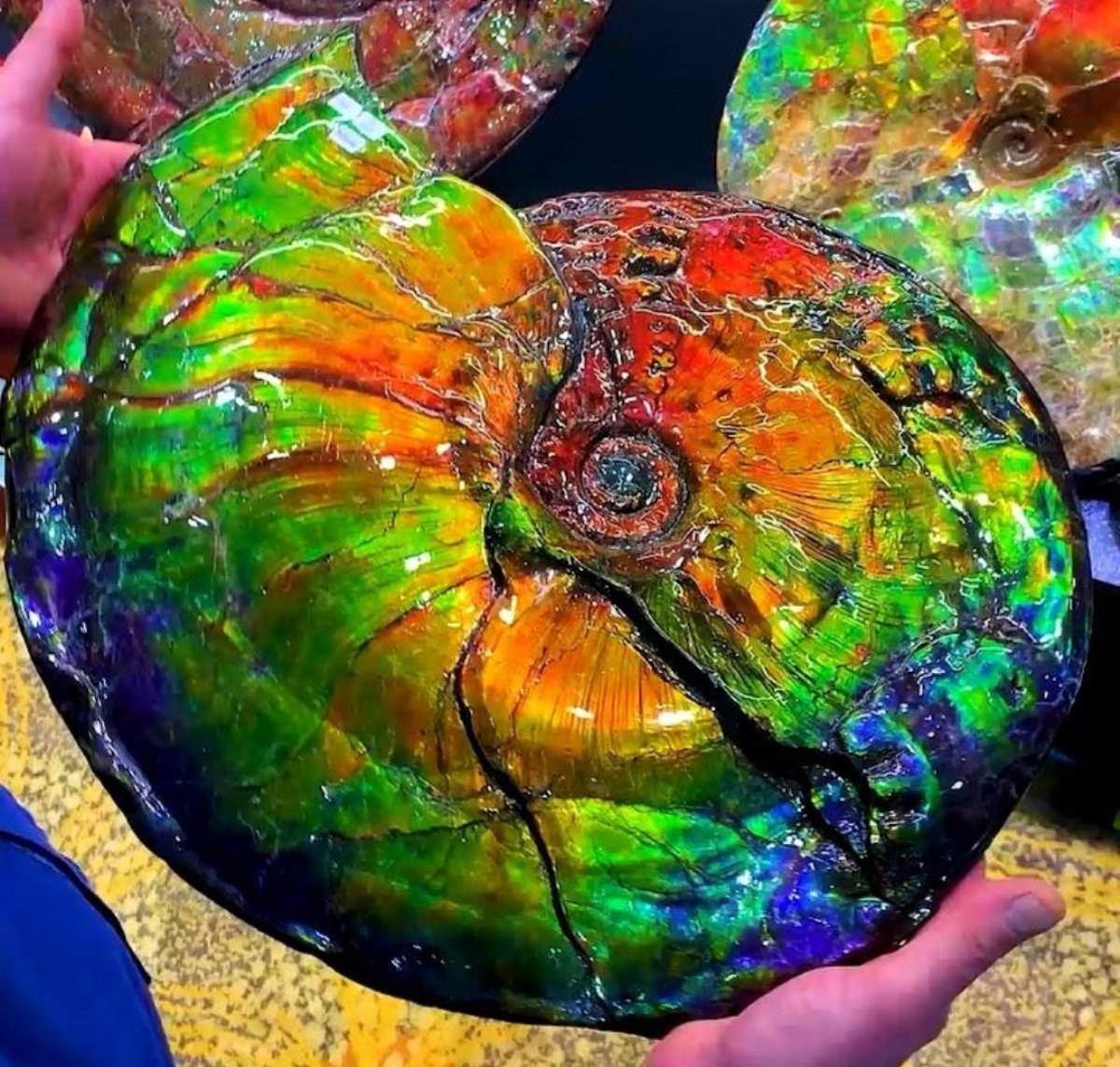
The Rare Ammolite with a spectacular flash of iridescent colors!
Ammolite is an opal-like organic gemstone found primarily along the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains of North America. It is made of the fossilized shells of ammonites, which in turn are composed primarily of aragonite, the same mineral contained in nacre, with a microstructure inherited from the shell. It is one of few biogenic gemstones; others include amber and pearl.
The chemical composition of ammolite is variable, and aside from aragonite may include calcite, silica, pyrite, or other minerals. The shell itself may contain a number of trace elements, including: aluminium; barium; chromium; copper; iron; magnesium; manganese; strontium; titanium; and vanadium. Its crystallography is orthorhombic. Its hardness is 4.5–5.5, and its specific gravity is 2.60–2.85.
An iridescent opal-like play of color is shown in fine specimens, mostly in shades of green and red; all the spectral colors are possible, however. The iridescence is due to the microstructure of the aragonite: unlike most other gems, whose colors come from light absorption, the iridescent color of ammolite comes from interference with the light that rebounds from stacked layers of thin platelets that make up the aragonite.
Significant deposits of gem-quality ammolite are only found in the Bearpaw Formation that extends from Alberta to Saskatchewan in Canada and south to Montana in the USA.The best grade of gem quality ammolite is along high energy river systems on the eastern slopes of the Rockies in southern Alberta. Most commercial mining operations have been conducted along the banks of the St. Mary River, in an area south of and between the town of Magrath and the city of Lethbridge.
The ammolite deposits in Canada
The ammolite deposits in Canada are located in the Bearpaw Formation, which extends from Alberta to Saskatchewan and into Montana. However, commercial extraction of the ammolite gemstone only occurs in Alberta, due to the superior grade of gem found in this region.
The Bearpaw Formation was once part of the Western Interior Seaway, a shallow sea that covered much of western North America during the Cretaceous period. Ammolite is formed from the fossilized shells of ammonites, a type of cephalopod that lived in this sea.
The ammolite deposits in Alberta are found in a narrow band along the eastern edge of the Rocky Mountains. The most important deposit is located near the town of Lethbridge. This deposit is known as the K Zone, and it is the only known source of gem-quality ammolite in the world.
The shallowest of these layers, named the "K Zone", lies some 15 meters below the surface and extends 30 meters down. The ammolite within this layer is covered by siderite concretions and is usually cracked—this is the crush material. It is the most common and (generally speaking) the least valuable of ammolite. Beginning twenty meters below the crush material is the "Blue Zone"; ammolite from this zone, which extends 65 meters, is usually compressed with a thin layer of pyrite rather than siderite concretions. This is the sheet material; due to its depth it is rarely mined. It is also much less fractured, and therefore the more valuable type of ammolite.