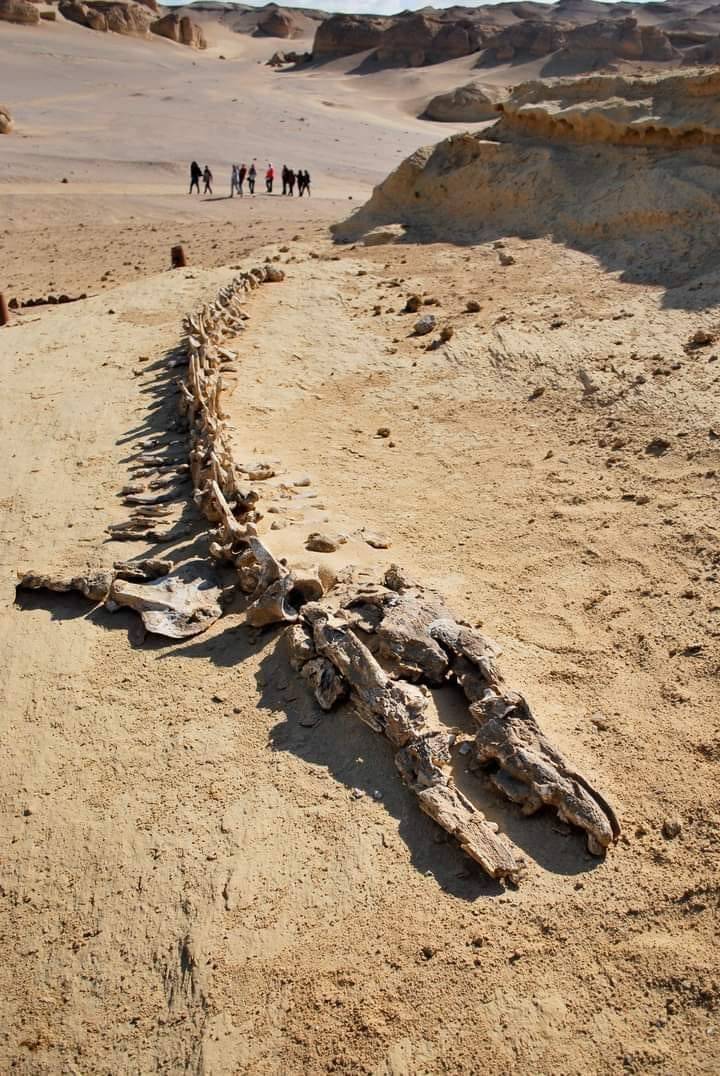
Fossil of 37 million years old whale skeleton (more than65ft long) Found in Wadi Al Hitan, Egyptian desert.
The fossils found at the site may not be the oldest but their great concentration in the area and the degree of their preservation is such that even some stomach contents are intact. The presence of fossils of other early animals such as sharks, crocodiles, sawfish, turtles and rays found at Wādī al-Ḥītān makes it possible to reconstruct the surrounding environmental and ecological conditions of the time, adding to its justification to be cited as a Heritage site.
The first fossil skeletons of whales were discovered in the winter of 1902–03.[1] For the next 80 years they attracted relatively little interest, largely due to the difficulty of reaching the area. In the 1980s interest in the site resumed as four wheel drive vehicles became more readily available. Continuing interest coincided with the site being visited by fossil collectors, and many bones were removed, prompting calls for the site to be conserved. The remains display the typical streamlined body form of modern whales, yet retaining some of the primitive aspects of skull and tooth structure. The largest skeleton found reached up to 21 m in length,[6] with well-developed five-fingered flippers on the forelimbs and the unexpected presence of hind legs, feet, and toes, not known previously in any archaeoceti. Their form was serpentine and they were carnivorous. A few of these skeletal remains are exposed but most are shallowly buried in sediments, slowly uncovered by erosion. Wādī al-Ḥītān provides evidences of millions of years of coastal marine life.
Wādī al-Ḥītān is the most important site in the world to demonstrate one of the iconic changes that make up the record of life on Earth: the evolution of the whales. It portrays vividly their form and mode of life during their transition from land animals to a marine existence. It exceeds the values of other comparable sites in terms of the number, concentration and quality of its fossils, and their accessibility and setting in an attractive and protected landscape. Iconic assemblage of fossilized skeletons of Archaeoceti (primitive whales documenting cetacean transition to marine life), sirenians and reptiles, as well as shark teeth from Gehannam Formation (40–41 million years ago).[7] The strata in Wādī al-Ḥītān belongs to Middle Eocene epoch and it contains extensive vertebrate fossils within a 200 km2 (77 sq mi) area. Fossils are present in high numbers and often show excellent quality of preservation. The most conspicuous fossils are the skeletons and bones of whales and sea cows, and over several hundred fossils of these have been documented.[8] Wādī al-Ḥītān (Whale Valley) is unusual in having such a large concentration of fossil whales (1500 marine vertebrate fossil skeletons) in a relatively small area.The fossils of whales vary from single bones to entire skeletons, and a number of partial skeletons are currently on display in the public part of the park. The two common whales are the large Basilosaurus, and the smaller (3- to 5-metre) Dorudon.[9] At least two other species are known from rarer remains. The whales possess small hind limbs, that are not seen in modern whales, and a powerful skull with teeth similar to those of carnivorous land mammals.[8] Other mammals are represented by the skeletons of three species of sirenia or sea cows. These were fully marine like the whales, and likewise show primitive features not seen in modern species and possess teeth that suggest that they grazed on seagrasses and other marine plants.[10] Bones of the primitive elephant Moeritherium have also been recorded.[
Advertisements
01 October 2023
Advertisements