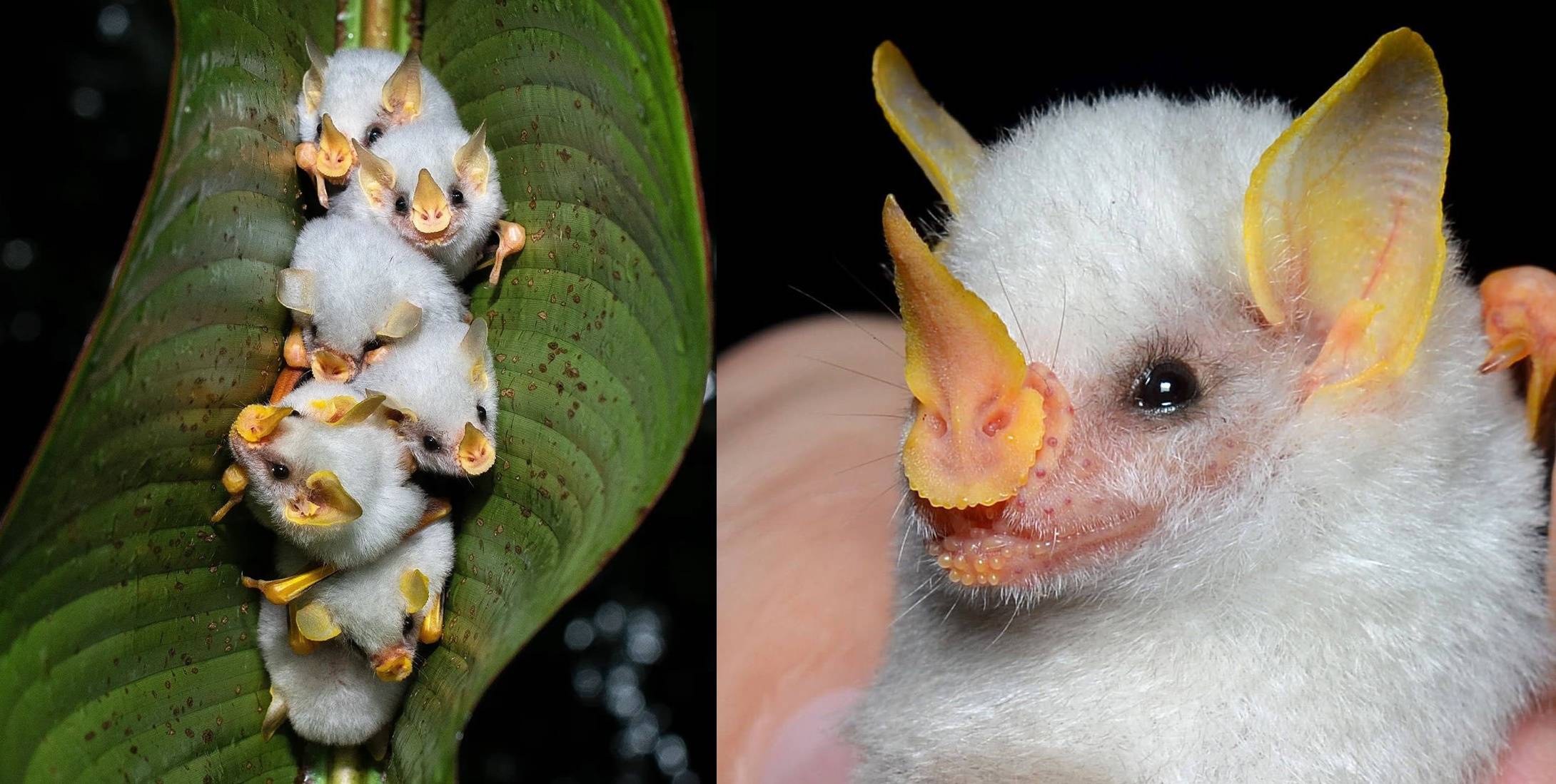
The Honduran white bat (Ectophylla alba)..
The Honduran White Bat is the first mammalian species known to incorporate carotenoids (a class of red, orange and yellow pigments found in plants) in their skin. The bright yellow color of their wings, ears, and nose comes from a yellow carotenoid pigment called lutein, which is probably attained by the bat’s diet of peeled fig fruits. Honduran White Bats are found only in Central America, ranging from Honduras through parts of eastern Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and western Panama. Also sometimes called the Honduran White Tent-making Bat, these small, leaf-nosed bats roost in leaf ‘tents’. Using their teeth, the bats cut along the ribs of Heliconia leaves to create a folded tent-like structure. Colonies tend to be small, with bats roosting in groups of two to 15 individuals.
Advertisements
03 April 2023
Advertisements