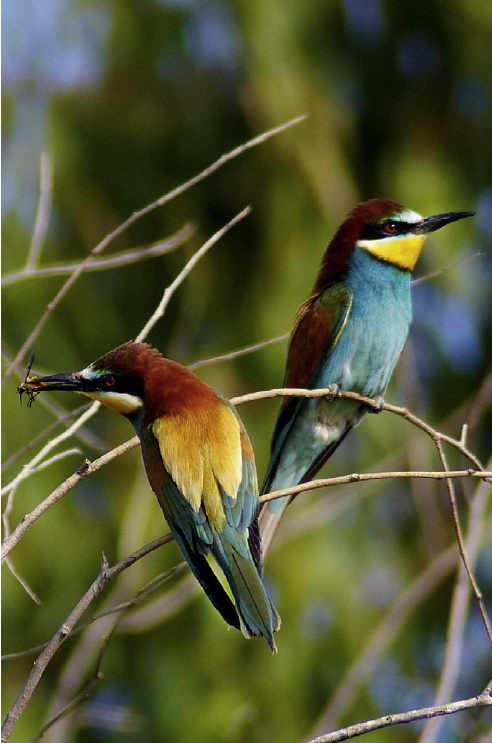
The European bee-eater (Merops apiaster)
The European bee-eater (Merops apiaster) is a near passerine bird in the bee-eater family, Meropidae. It breeds in southern Europe and in parts of north Africa and western Asia. It is strongly migratory, wintering in tropical Africa. This species occurs as a spring overshoot north of its range, with occasional breeding in northwest Europe.
Many bee-keepers believe that the bee-eaters are the main obstacle causing worker bees not to forage, and instead stay inside the hives for much of the day between May and the end of August. However, a study carried out in eucalyptus forest in the Alalous region, 80 km (50 mi) east of Tripoli Libya, showed that the bee-eaters were not the main obstacle of bee foraging, which is the opposite of what beekeepers think. The foraging rate was higher in presence of the birds than in their absence in some cases. The average bird meal consisted of 90.8% honey bees and 9.2% beetles.
Predation is more likely when the bees are queening or during peak migrations, from late March till mid-April, and in mid-September. Hives close to or under trees or overhead cables are also at increased risk as the birds pounce on flying insects from these perches.
Advertisements
09 October 2022
Advertisements