The Oldest Wooden Staircase Ever Found Dates Back to 3,400 Years Ago and Is Perfectly Preserved
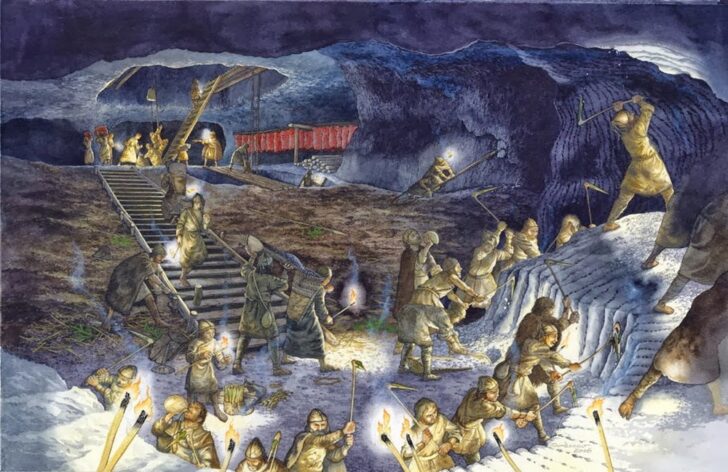
Hallstatt mining in the Bronze Age. Image credit: H. Reschreiter – D. Groebner/Naturhistorisches Museum Wien
The staircase extends over 8 meters (26 ft) and was designed as an aid to get over huge heaps of mining waste, upon which it rested. The woodworking traces preserved in the material show that the wood was not chiseled or cut with an adze, but was rather created by transverse cutting using a bronze axe.
Although, as noted above, the construction is absolutely unique and not found in other mines (for instance prehistoric copper mines), the stairway in the Christian von Tuschwerk is not a completely isolated case within the Hallstatt salt mine itself. Parts of such stairs have been discovered in other parts of the mine, suggesting that such staircases were the access equipment of choice for salt mining in the Bronze Age. There were probably two variants, a wide construction supported on the mining waste and used mainly for salt transport, and a narrower version in the shafts for personnel access only.
The staircase extends over 8 meters (26 ft) and was designed as an aid to get over huge heaps of mining waste, upon which it rested. The woodworking traces preserved in the material show that the wood was not chiseled or cut with an adze, but was rather created by transverse cutting using a bronze axe.
Although, as noted above, the construction is absolutely unique and not found in other mines (for instance prehistoric copper mines), the stairway in the Christian von Tuschwerk is not a completely isolated case within the Hallstatt salt mine itself. Parts of such stairs have been discovered in other parts of the mine, suggesting that such staircases were the access equipment of choice for salt mining in the Bronze Age. There were probably two variants, a wide construction supported on the mining waste and used mainly for salt transport, and a narrower version in the shafts for personnel access only.
Advertisements
18 November 2023
Advertisements