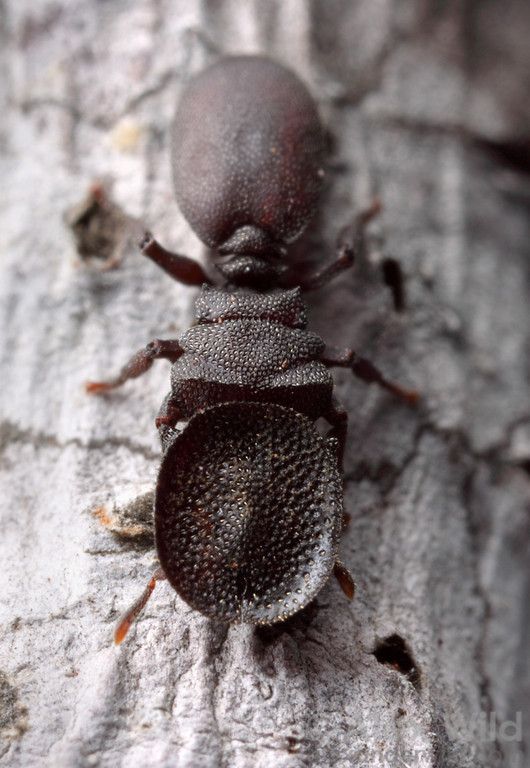
A Tale of Turtle Ants and Soldier Evolution
In the study, the authors focus on the concept of “disruptive selection”. Disruptive selection is a type of natural selection that favors extreme phenotypes and/or selects against intermediate or mean phenotypes. This process can be promoted by intraspecific competition – it may be advantageous to have traits that are different from a competitor in order to utilize some resource without the cost of competing for that resource. The expected outcome of disruptive selection is the evolution of two separate phenotypes within a population, which may then lead to the evolution of new species.
Advertisements
23 August 2022
Advertisements